11 KiB
Windows 10 Home VS Pro
-
Features: Windows 10 Pro has a number of features that are not available in Windows 10 Home, including support for Remote Desktop, the ability to join a domain, and support for BitLocker drive encryption.
-
Updates: Windows 10 Pro receives updates at a faster rate than Windows 10 Home. This means that Pro users will get access to new features and security updates more quickly.
-
Licensing: Windows 10 Home is designed for personal use and can only be installed on a single device. Windows 10 Pro can be installed on multiple devices and is suitable for businesses or organizations.
-
Price: Windows 10 Home is generally less expensive than Windows 10 Pro.
- This mean that all the windows machine connected to an active directory are windows pro
Windows Server VS Operating System
Windows Server 2019 is a version of the Windows operating system that is used to host web sites, applications, and services in a server environment. It is designed for use in a networked environment and includes features such as server virtualization and remote desktop services.
On the other hand, a Windows operating system running on a computer is used for personal or business purposes and is not designed for use in a server environment. It is typically used to run desktop applications and perform tasks such as browsing the Internet, creating and editing documents, and playing games.
New Technology File System (NTFS) and Alternate Data Streams (ADS)
NTFS (New Technology File System) is a file system that is used by the Microsoft Windows operating system to store and manage files on a hard drive or other storage device. NTFS was introduced with Windows NT and has since been used as the default file system for all versions of Windows.
One of the main features of NTFS is that it supports file and folder permissions, which allow you to control who can access and modify files and folders on your computer. This is particularly useful in a business or enterprise environment, where multiple users may need to access shared resources.
NTFS addresses many of the limitations of the previous file systems; such as:
- Supports files larger than 4GB
- Set specific permissions on folders and files
- Folder and file compression
- Encryption (Encryption File System or EFS)
On NTFS volumes, you can set permissions that grant or deny access to files and folders.
The permissions are:
-
Full control: This permission allows the user to do anything with the file or folder, including reading, writing, modifying, and deleting it. This permission also allows the user to change the permissions on the file or folder.
-
Modify: This permission allows the user to read, write, and delete the file or folder, but does not allow them to change the permissions.
-
Read & Execute: This permission allows the user to read the contents of the file or folder, and to run files as programs if they are executable. It does not allow the user to write to or delete the file or folder.
-
List folder contents: This permission allows the user to view the contents of a folder, but does not allow them to access the files or subfolders within the folder.
-
Read: This permission allows the user to read the contents of the file or folder, but does not allow them to write to or delete the file or folder.
-
Write: This permission allows the user to write to the file or folder, but does not allow them to read or delete it.
In the Microsoft Windows operating system, alternate data streams (ADS) are a feature of the NTFS file system that allows you to store additional data within a file, in addition to the file's main data stream. This additional data is stored in a separate stream within the file, and is not visible when the file is accessed using normal methods.
ADS were originally intended to be used as a way to store metadata and other information about a file, such as the file's author or creation date. However, they can also be used to store malicious or unwanted data, such as malware or spam.
Because ADS are not visible when a file is accessed in the normal way, they can be used by attackers to hide malicious code or other unwanted content within a file. This can make it difficult to detect and remove such content, as it is not visible when the file is accessed or scanned using standard tools.
To protect against the potential risks posed by ADS, it is important to use antivirus software and other security tools that are designed to detect and remove malicious content that may be hidden in alternate data streams. In addition, you should be careful when downloading and opening files from untrusted sources, as these files may contain hidden ADS that could contain malicious content.
In the Microsoft Windows operating system, you can use the "type" command in the command prompt to create an alternate data stream (ADS) within a file. To do this:
- Open the command prompt.
- Navigate to the folder that contains the file that you want to add an ADS to.
- Type the following command: Text ---> "type HidenTEXT > file.txt:HidenTEXT" File ---> "type Hidenfile.txt > file.txt:Hidenfile.txt" Delete the file Hidenfile.txt
To open the file and see the hiden element, simply type
EDITOR-OF-CHOICE file.txt:HidenTEXT or file.txt:Hidenfile.txt
See i f a folder contain any ADS
dir /r
Replace "HidenTEXT" or "Hidenfile" with the text that you want to add to the ADS, "filename" with the name of the file that you want to add the ADS to, and "HidenTEXT" with the name that you want to give to the ADS.
Windows\System32 Folders
This is where environment variables, more specifically system environment variables, come into play. The system environment variable for the Windows directory is %windir%.
The System32 folder holds the important files that are critical for the operating system.
User Accounts, Profiles, and Permissions
User accounts can be one of two types on a typical local Windows system: Administrator & Standard User.
The user account type will determine what actions the user can perform on that specific Windows system.
- An Administrator can make changes to the system: add users, delete users, modify groups, modify settings on the system, etc.
Check all the user on the compute
lusrmgr.msc
Type of groups and users Local Groups Local Users
Remote Groups (Active Directory) Remote Users (Active Directory)
Settings & Management
The System Configuration utility (MSConfig) is for advanced troubleshooting, and its main purpose is to help diagnose startup issues.
The utility has five tabs across the top. Below are the names for each tab. We will briefly cover each tab in this task.
- General
- Boot
- Services
- Startup
- Tools
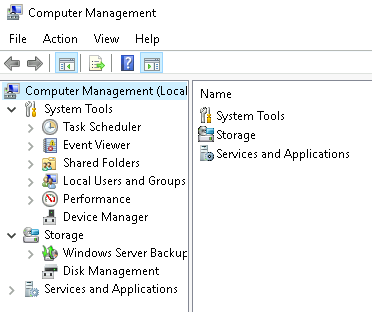
The Computer Management (compmgmt) utility has three primary sections: System Tools, Storage, and Services and Applications.
-
System Tools Task Scheduler A task can run an application, a script, etc., and tasks can be configured to run at any point. A task can run at log in or at log off. Tasks can also be configured to run on a specific schedule, for example, every five mins. Event Viewer Event Viewer allows us to view events that have occurred on the computer. These records of events can be seen as an audit trail that can be used to understand the activity of the computer system. This information is often used to diagnose problems and investigate actions executed on the system. Shared Folders where you will see a complete list of shares and folders shared that others can connect to. Local Users and Groups Show users and group policy Performance Perfmon is used to view performance data either in real-time or from a log file. This utility is useful for troubleshooting performance issues on a computer system, whether local or remote. Device Manager Allows us to view and configure the hardware, such as disabling any hardware attached to the computer.
-
Storage Under Storage is Windows Server Backup and Disk Management. Disk Management is a system utility in Windows that enables you to perform advanced storage tasks. Some tasks are: - Set up a new drive - Extend a partition - Shrink a partition - Assign or change a drive letter (ex. E:)
-
Services and Applications Here you can do more than enable and disable a service, such as view the Properties for the service.
This tool gathers information about your computer and displays a comprehensive view of your hardware, system components, and software environment, which you can use to diagnose computer issues.
The information in System Summary is divided into three sections:
- Hardware Resources
- Components
- Software Environment
Environment Variable (Software Environment) Environment variables store information about the operating system environment. This information includes details such as the operating system path, the number of processors used by the operating system, and the location of temporary folders.
Resource Monitor displays per-process and aggregate CPU, memory, disk, and network usage information, in addition to providing details about which processes are using individual file handles and modules.
In the Overview tab, Resmon has four sections:
- CPU
- Disk
- Network
- Memory
The Windows Registry (per Microsoft) is a central hierarchical database used to store information necessary to configure the system for one or more users, applications, and hardware devices.
The registry contains information that Windows continually references during operation, such as:
- Profiles for each user
- Applications installed on the computer and the types of documents that each can create
- Property sheet settings for folders and application icons
- What hardware exists on the system
- The ports that are being used.
Other Elements
Traffic flows into and out of devices via what we call ports. A firewall is what controls what is - and more importantly isn't - allowed to pass through those ports. You can think of it like a security guard standing at the door, checking the ID of everything that tries to enter or exit
The Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) coordinates the required actions to create a consistent shadow copy (also known as a snapshot or a point-in-time copy) of the data that is to be backed up.
Volume Shadow Copies are stored on the System Volume Information folder on each drive that has protection enabled.
If VSS is enabled (System Protection turned on), you can perform the following tasks from within advanced system settings.
- Create a restore point
- Perform system restore
- Configure restore settings
- Delete restore points