Data Structure Typed







Data Structures of Javascript & TypeScript.
Do you envy C++ with STL, Python with collections, and Java with java.util ? Well, no need to envy anymore! JavaScript and TypeScript now have data-structure-typed.
Now you can use this library in Node.js and browser environments in CommonJS(require export.modules = ), ESModule(import export), Typescript(import export), UMD(var Queue = dataStructureTyped.Queue)
Built-in classic algorithms
DFS(Depth-First Search), DFSIterative, BFS(Breadth-First Search), morris, Bellman-Ford Algorithm, Dijkstra's Algorithm,
Floyd-Warshall Algorithm, Tarjan's Algorithm.
Installation and Usage
npm
npm i data-structure-typed --save
yarn
yarn add data-structure-typed
import {
BinaryTree, Graph, Queue, Stack, PriorityQueue, BST, Trie, DoublyLinkedList,
AVLTree, MinHeap, SinglyLinkedList, DirectedGraph, TreeMultiset,
DirectedVertex, AVLTreeNode
} from 'data-structure-typed';
CDN
<script src='https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/data-structure-typed/dist/umd/data-structure-typed.min.js'></script>
const {Heap} = dataStructureTyped;
const {
BinaryTree, Graph, Queue, Stack, PriorityQueue, BST, Trie, DoublyLinkedList,
AVLTree, MinHeap, SinglyLinkedList, DirectedGraph, TreeMultiset,
DirectedVertex, AVLTreeNode
} = dataStructureTyped;
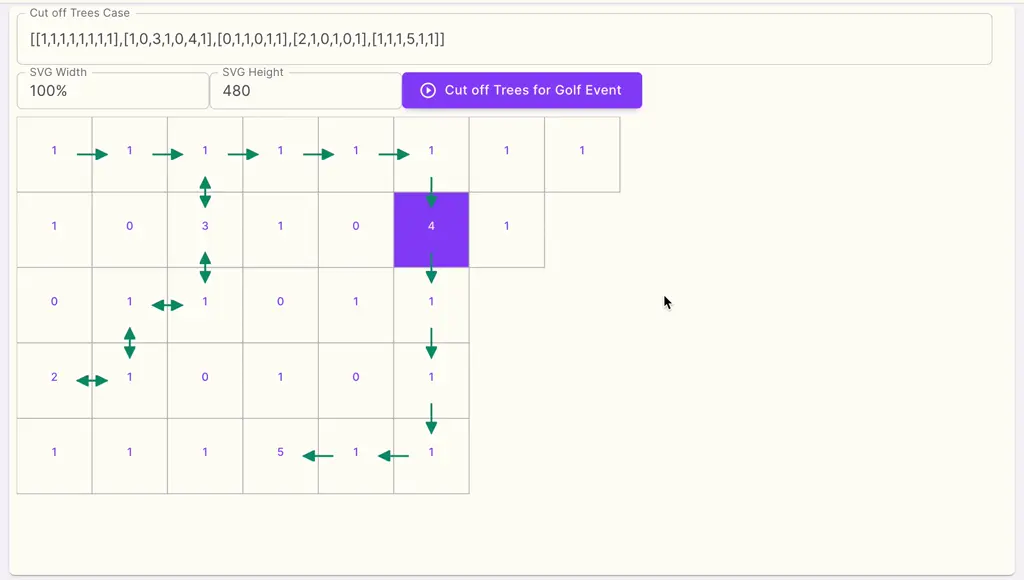
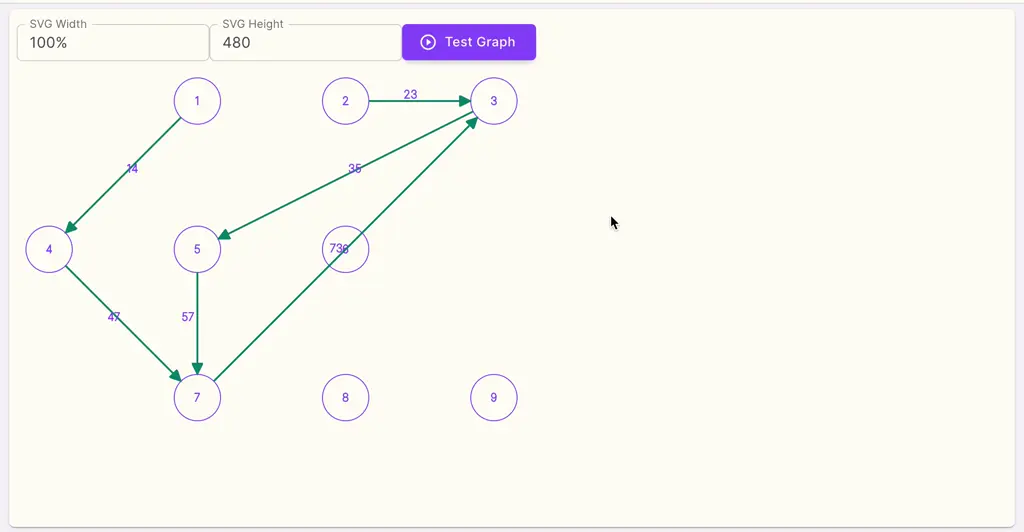
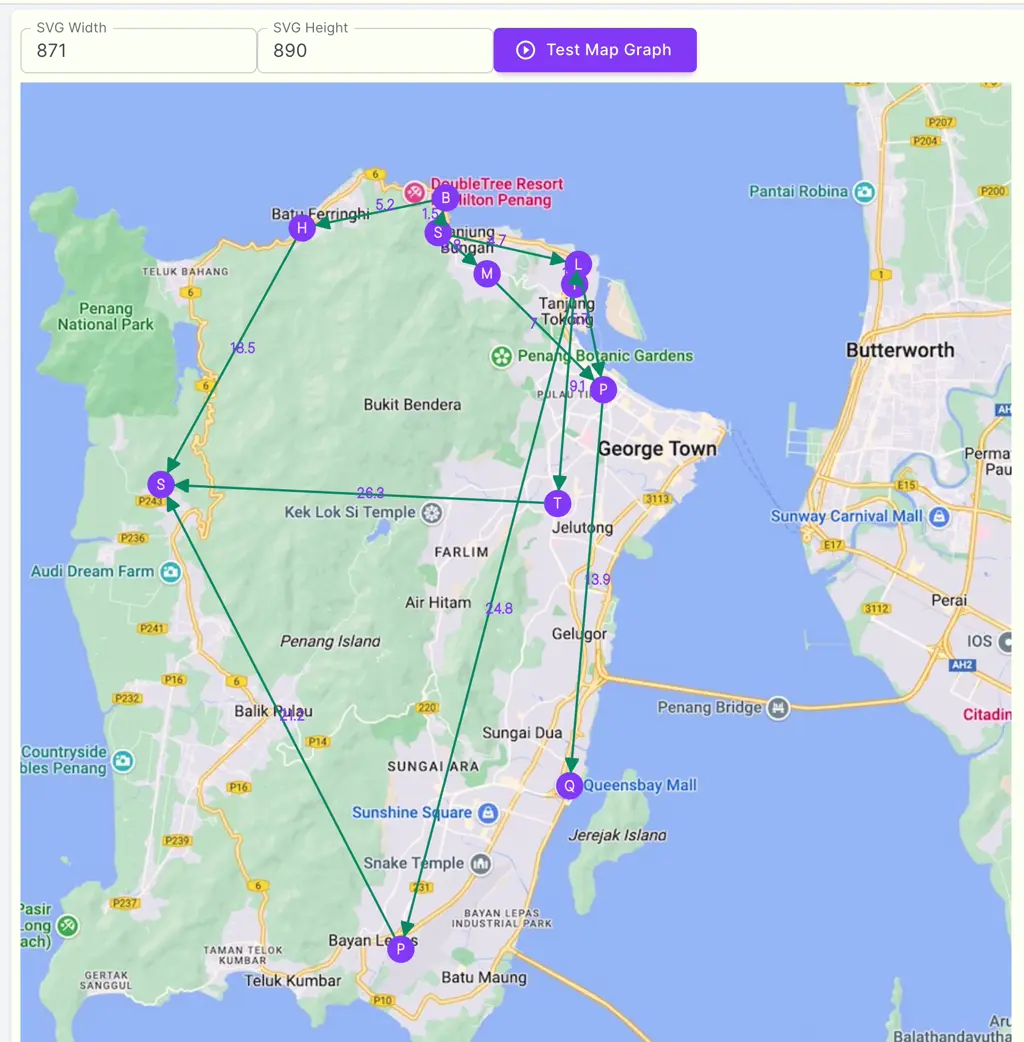
API docs & Examples
API Docs
Live Examples
Examples Repository
Code Snippet
Binary Search Tree (BST) snippet
TS
import {BST, BSTNode} from 'data-structure-typed';
const bst = new BST();
bst.add(11);
bst.add(3);
bst.addMany([15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5]);
bst.size === 16; // true
bst.has(6); // true
const node6 = bst.get(6); // BSTNode
bst.getHeight(6) === 2; // true
bst.getHeight() === 5; // true
bst.getDepth(6) === 3; // true
bst.getLeftMost()?.id === 1; // true
bst.delete(6);
bst.get(6); // null
bst.isAVLBalanced(); // true
bst.bfs()[0] === 11; // true
const objBST = new BST<BSTNode<{id: number, keyA: number}>>();
objBST.add(11, {id: 11, keyA: 11});
objBST.add(3, {id: 3, keyA: 3});
objBST.addMany([{id: 15, keyA: 15}, {id: 1, keyA: 1}, {id: 8, keyA: 8},
{id: 13, keyA: 13}, {id: 16, keyA: 16}, {id: 2, keyA: 2},
{id: 6, keyA: 6}, {id: 9, keyA: 9}, {id: 12, keyA: 12},
{id: 14, keyA: 14}, {id: 4, keyA: 4}, {id: 7, keyA: 7},
{id: 10, keyA: 10}, {id: 5, keyA: 5}]);
objBST.delete(11);
JS
const {BST, BSTNode} = require('data-structure-typed');
const bst = new BST();
bst.add(11);
bst.add(3);
bst.addMany([15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5]);
bst.size === 16; // true
bst.has(6); // true
const node6 = bst.get(6);
bst.getHeight(6) === 2; // true
bst.getHeight() === 5; // true
bst.getDepth(6) === 3; // true
const leftMost = bst.getLeftMost();
leftMost?.id === 1; // true
expect(leftMost?.id).toBe(1);
bst.delete(6);
bst.get(6); // null
bst.isAVLBalanced(); // true or false
const bfsIDs = bst.bfs();
bfsIDs[0] === 11; // true
expect(bfsIDs[0]).toBe(11);
const objBST = new BST();
objBST.add(11, {id: 11, keyA: 11});
objBST.add(3, {id: 3, keyA: 3});
objBST.addMany([{id: 15, keyA: 15}, {id: 1, keyA: 1}, {id: 8, keyA: 8},
{id: 13, keyA: 13}, {id: 16, keyA: 16}, {id: 2, keyA: 2},
{id: 6, keyA: 6}, {id: 9, keyA: 9}, {id: 12, keyA: 12},
{id: 14, keyA: 14}, {id: 4, keyA: 4}, {id: 7, keyA: 7},
{id: 10, keyA: 10}, {id: 5, keyA: 5}]);
objBST.delete(11);
const avlTree = new AVLTree();
avlTree.addMany([11, 3, 15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5])
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
avlTree.delete(10);
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
AVLTree snippet
TS
import {AVLTree} from 'data-structure-typed';
const avlTree = new AVLTree();
avlTree.addMany([11, 3, 15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5])
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
avlTree.delete(10);
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
JS
const {AVLTree} = require('data-structure-typed');
const avlTree = new AVLTree();
avlTree.addMany([11, 3, 15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5])
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
avlTree.delete(10);
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
Directed Graph simple snippet
TS or JS
import {DirectedGraph} from 'data-structure-typed';
const graph = new DirectedGraph();
graph.addVertex('A');
graph.addVertex('B');
graph.hasVertex('A'); // true
graph.hasVertex('B'); // true
graph.hasVertex('C'); // false
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.hasEdge('A', 'B'); // true
graph.hasEdge('B', 'A'); // false
graph.deleteEdgeSrcToDest('A', 'B');
graph.hasEdge('A', 'B'); // false
graph.addVertex('C');
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.addEdge('B', 'C');
const topologicalOrderIds = graph.topologicalSort(); // ['A', 'B', 'C']
Undirected Graph snippet
TS or JS
import {UndirectedGraph} from 'data-structure-typed';
const graph = new UndirectedGraph();
graph.addVertex('A');
graph.addVertex('B');
graph.addVertex('C');
graph.addVertex('D');
graph.deleteVertex('C');
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.addEdge('B', 'D');
const dijkstraResult = graph.dijkstra('A');
Array.from(dijkstraResult?.seen ?? []).map(vertex => vertex.id) // ['A', 'B', 'D']
Data Structures
Standard library data structure comparison
| Data Structure Typed |
C++ STL |
java.util |
Python collections |
| Array<E> |
vector<T> |
ArrayList<E> |
list |
| DoublyLinkedList<E> |
list<T> |
LinkedList<E> |
deque |
| SinglyLinkedList<E> |
- |
- |
- |
| Set<E> |
set<T> |
HashSet<E> |
set |
| Map<K, V> |
map<K, V> |
HashMap<K, V> |
dict |
| Map<K, V> |
- |
- |
OrderedDict |
| Queue<E> |
queue<T> |
Queue<E> |
- |
| PriorityQueue<E> |
priority_queue<T> |
PriorityQueue<E> |
- |
| Heap<V> |
priority_queue<T> |
PriorityQueue<E> |
heapq |
| Stack<E> |
stack<T> |
Stack<E> |
- |
| Deque<E> |
deque<T> |
- |
- |
| Trie |
- |
- |
- |
| HashMap<K, V> |
unordered_map<K, V> |
HashMap<K, V> |
defaultdict |
| - |
multiset<T> |
- |
- |
| - |
multimap<K, V> |
- |
- |
| BinaryTree<K, V> |
- |
- |
- |
| BST<K, V> |
- |
- |
- |
| DirectedGraph<V, E> |
- |
- |
- |
| UndirectedGraph<V, E> |
- |
- |
- |
| - |
unordered_multiset |
- |
Counter |
| - |
- |
LinkedHashSet<E> |
- |
| - |
- |
LinkedHashMap<K, V> |
- |
| AVLTree<E> |
- |
TreeSet<E> |
- |
| AVLTree<K, V> |
- |
TreeMap<K, V> |
- |
| AVLTree<E> |
set |
TreeSet<E> |
- |
| - |
unordered_multimap<K, V> |
- |
- |
| - |
bitset<N> |
- |
- |
| - |
unordered_set<T> |
HashSet<E> |
- |
Code design
Adhere to ES6 standard naming conventions for APIs.
Standardize API conventions by using 'add' and 'delete' for element manipulation methods in all data structures.
Opt for concise and clear method names, avoiding excessive length while ensuring explicit intent.
Object-oriented programming(OOP)
By strictly adhering to object-oriented design (BinaryTree -> BST -> AVLTree -> TreeMultiset), you can seamlessly
inherit the existing data structures to implement the customized ones you need. Object-oriented design stands as the
optimal approach to data structure design.
Benchmark
avl-tree
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|
| 10,000 add randomly | 31.93 | 31.32 | 2.30e-4 |
| 10,000 add & delete randomly | 69.12 | 14.47 | 0.00 |
| 10,000 addMany | 41.14 | 24.31 | 1.60e-4 |
| 10,000 get | 28.68 | 34.86 | 7.65e-4 |
binary-tree
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|
| 1,000 add randomly | 13.12 | 76.21 | 3.40e-4 |
| 1,000 add & delete randomly | 16.33 | 61.22 | 4.17e-4 |
| 1,000 addMany | 10.96 | 91.22 | 3.99e-4 |
| 1,000 get | 18.65 | 53.63 | 4.20e-4 |
| 1,000 dfs | 71.82 | 13.92 | 0.00 |
| 1,000 bfs | 58.95 | 16.96 | 0.00 |
| 1,000 morris | 37.46 | 26.70 | 4.60e-4 |
bst
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|
| 10,000 add randomly | 32.98 | 30.32 | 0.00 |
| 10,000 add & delete randomly | 74.47 | 13.43 | 0.00 |
| 10,000 addMany | 29.93 | 33.41 | 6.02e-4 |
| 10,000 get | 29.92 | 33.42 | 8.61e-4 |
rb-tree
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|
| 100,000 add randomly | 80.49 | 12.42 | 0.01 |
| 100,000 add & 1000 delete randomly | 89.97 | 11.11 | 0.01 |
| 100,000 getNode | 68.63 | 14.57 | 0.01 |
directed-graph
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|
| 1,000 addVertex | 0.10 | 9878.72 | 1.87e-6 |
| 1,000 addEdge | 6.34 | 157.78 | 2.53e-4 |
| 1,000 getVertex | 0.05 | 2.12e+4 | 1.05e-6 |
| 1,000 getEdge | 23.08 | 43.33 | 0.00 |
| tarjan | 217.75 | 4.59 | 0.01 |
| tarjan all | 219.23 | 4.56 | 0.01 |
| topologicalSort | 175.73 | 5.69 | 0.02 |
heap
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|
| 10,000 add & pop | 4.64 | 215.44 | 6.89e-5 |
| 10,000 fib add & pop | 357.37 | 2.80 | 0.01 |
doubly-linked-list
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|
| 1,000,000 unshift | 239.34 | 4.18 | 0.04 |
| 1,000,000 unshift & shift | 168.74 | 5.93 | 0.04 |
| 1,000,000 insertBefore | 324.74 | 3.08 | 0.06 |
singly-linked-list
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|
| 10,000 push & pop | 213.86 | 4.68 | 0.01 |
| 10,000 insertBefore | 254.02 | 3.94 | 0.02 |
max-priority-queue
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|
| 10,000 refill & poll | 11.39 | 87.76 | 2.14e-4 |
deque
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|
| 1,000,000 push | 233.91 | 4.28 | 0.05 |
| 1,000,000 shift | 25.61 | 39.05 | 0.00 |
queue
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|
| 1,000,000 push | 43.88 | 22.79 | 0.01 |
| 1,000,000 push & shift | 81.71 | 12.24 | 0.00 |
trie
| test name | time taken (ms) | executions per sec | sample deviation |
|---|
| 100,000 push | 59.93 | 16.69 | 0.01 |
| 100,000 getWords | 93.10 | 10.74 | 0.01 |
















































































