data-structure-typed
What




Brief
Data Structures of Javascript & TypeScript.
Built-in classic algorithms
DFS(Depth-First Search), DFSIterative, BFS(Breadth-First Search), morris, Bellman-Ford Algorithm, Dijkstra's Algorithm, Floyd-Warshall Algorithm, Tarjan's Algorithm.
How
install
npm
npm install data-structure-typed --save
yarn
yarn add data-structure-typed
CDN
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/data-structure-typed/umd/bundle.min.js"></script>
const {AVLTree} = dataStructureTyped;
const {Heap, MinHeap, SinglyLinkedList, Stack, AVLTreeNode, BST, Trie, DirectedGraph, DirectedVertex, TreeMultiset} = dataStructureTyped;
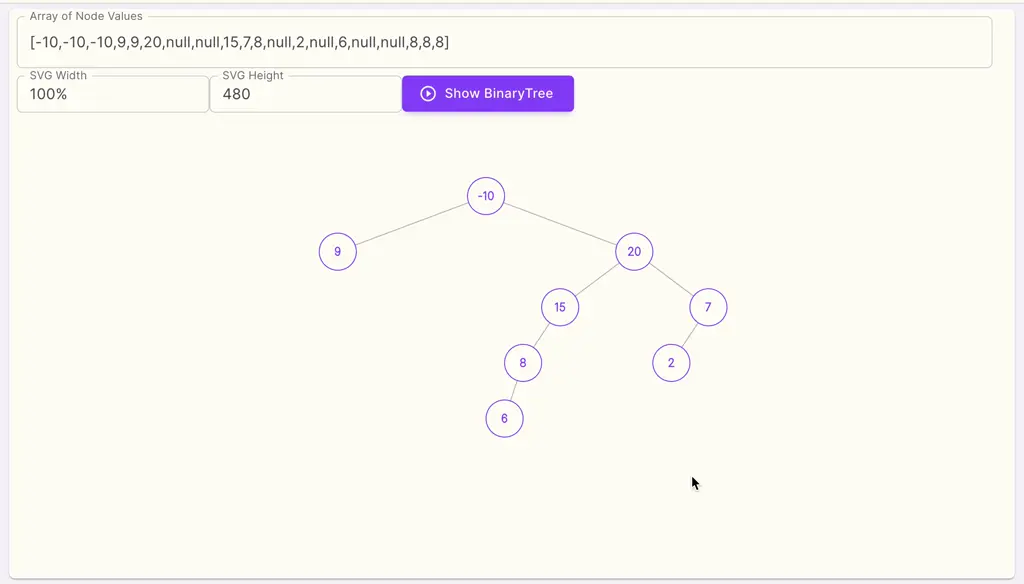
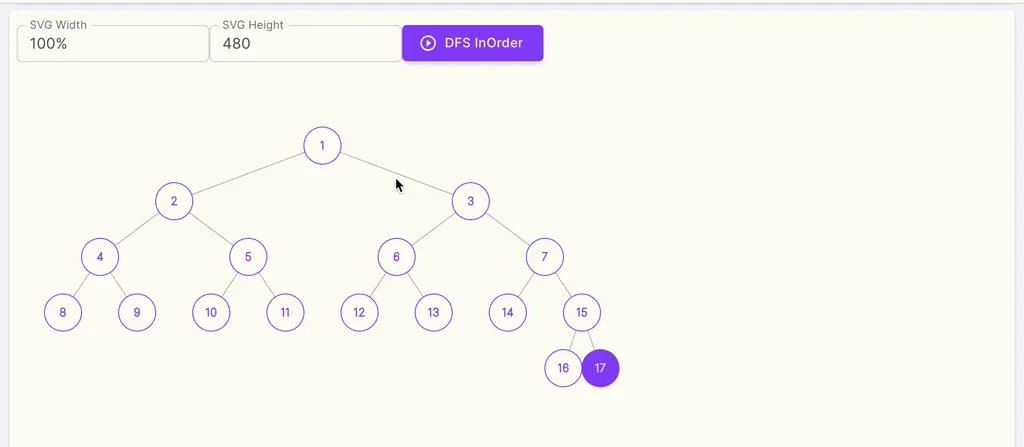
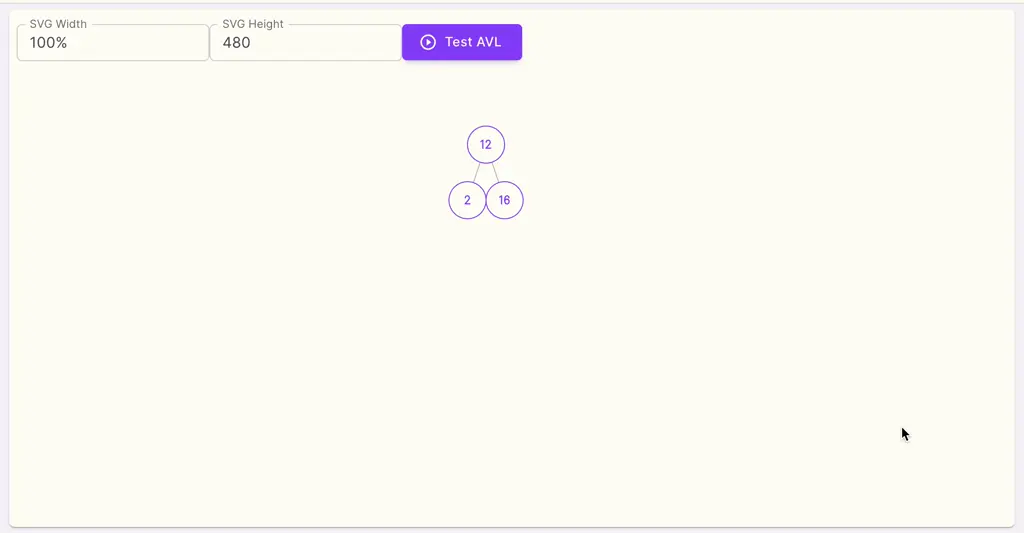
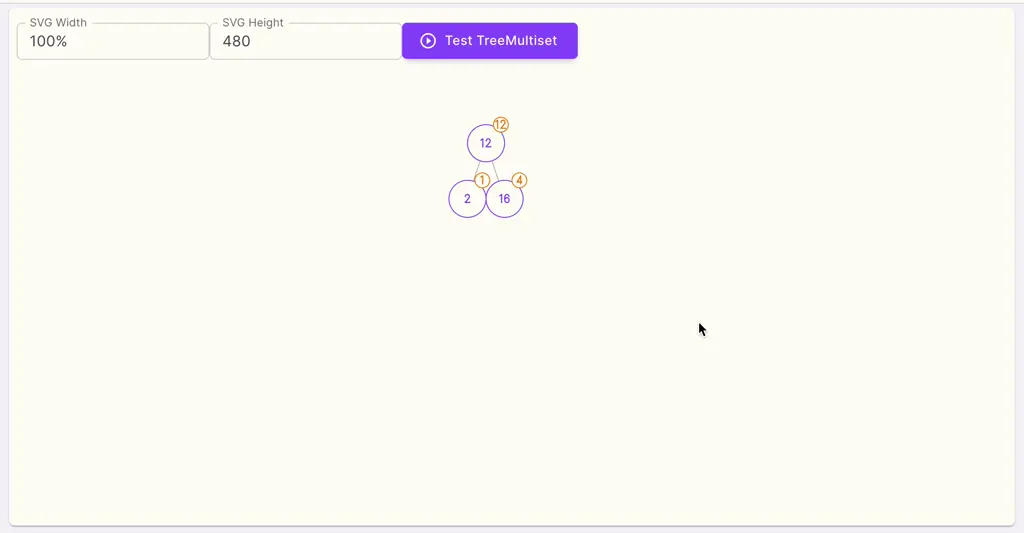
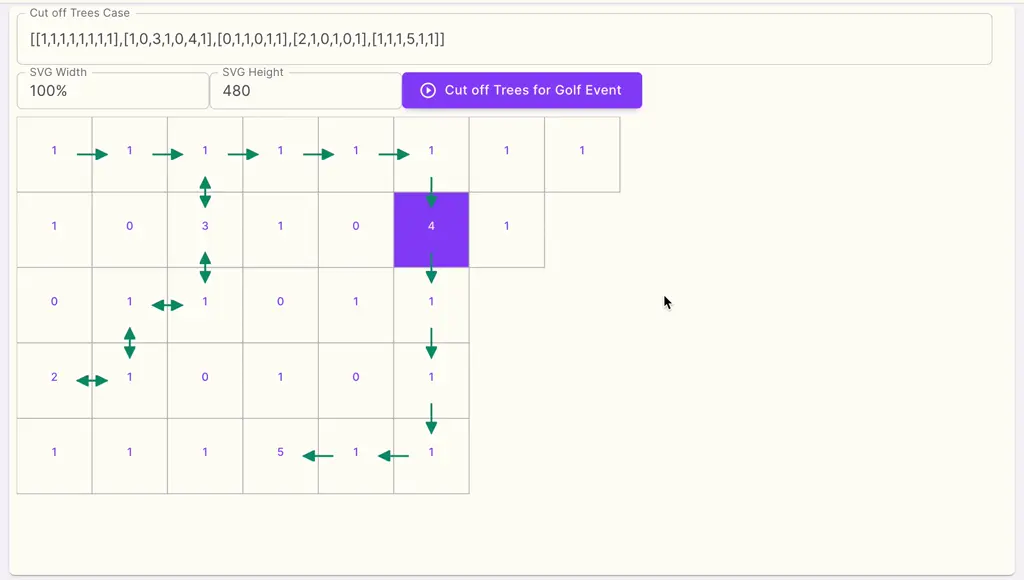
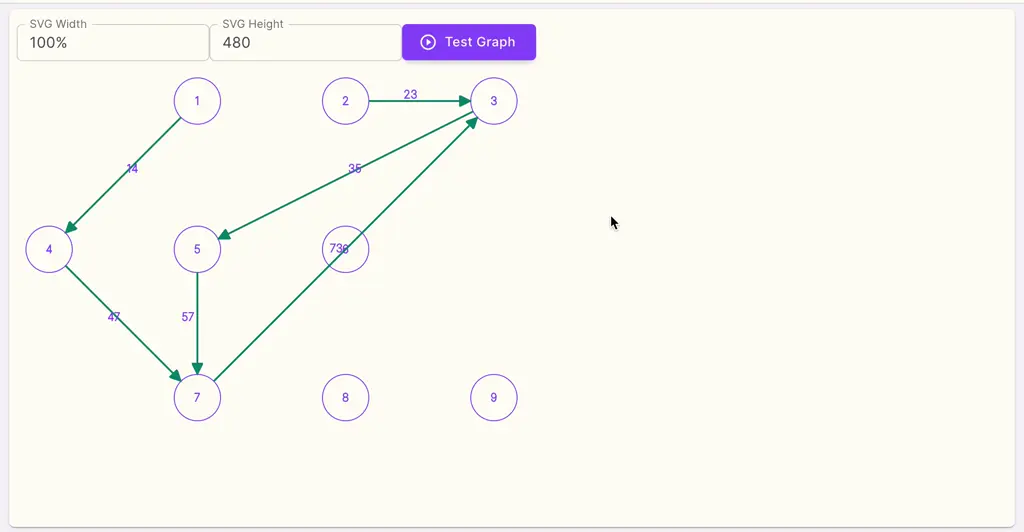
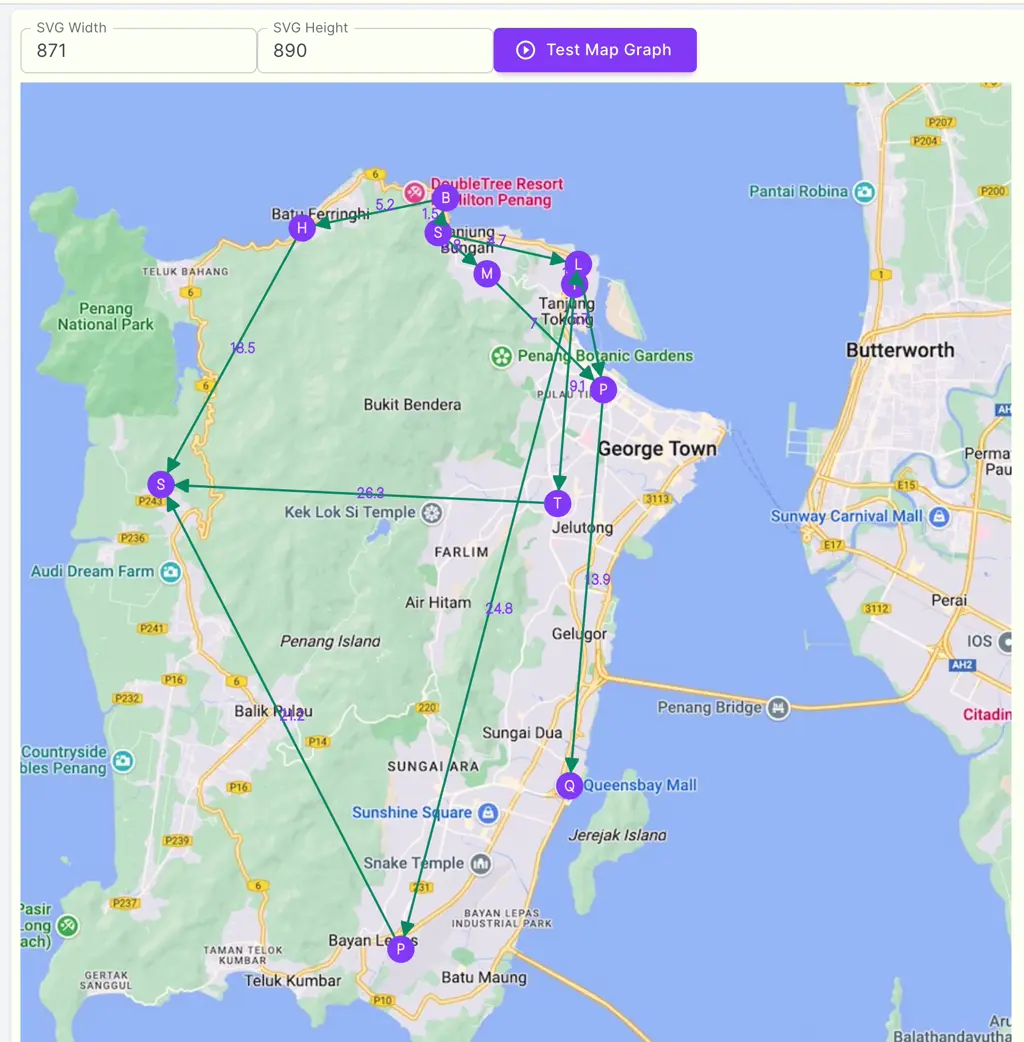
API docs & Examples
Code Snippet
Binary Search Tree (BST) snippet
TS
import {BST, BSTNode} from 'data-structure-typed';
const bst = new BST();
bst.add(11);
bst.add(3);
bst.addMany([15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5]);
bst.size === 16; // true
bst.has(6); // true
const node6 = bst.get(6); // BSTNode
bst.getHeight(6) === 2; // true
bst.getHeight() === 5; // true
bst.getDepth(6) === 3; // true
bst.getLeftMost()?.id === 1; // true
bst.remove(6);
bst.get(6); // null
bst.isAVLBalanced(); // true
bst.BFS()[0] === 11; // true
const objBST = new BST<BSTNode<{ id: number, keyA: number }>>();
objBST.add(11, {id: 11, keyA: 11});
objBST.add(3, {id: 3, keyA: 3});
objBST.addMany([{id: 15, keyA: 15}, {id: 1, keyA: 1}, {id: 8, keyA: 8},
{id: 13, keyA: 13}, {id: 16, keyA: 16}, {id: 2, keyA: 2},
{id: 6, keyA: 6}, {id: 9, keyA: 9}, {id: 12, keyA: 12},
{id: 14, keyA: 14}, {id: 4, keyA: 4}, {id: 7, keyA: 7},
{id: 10, keyA: 10}, {id: 5, keyA: 5}]);
objBST.remove(11);
JS
const {BST, BSTNode} = require('data-structure-typed');
const bst = new BST();
bst.add(11);
bst.add(3);
bst.addMany([15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5]);
bst.size === 16; // true
bst.has(6); // true
const node6 = bst.get(6);
bst.getHeight(6) === 2; // true
bst.getHeight() === 5; // true
bst.getDepth(6) === 3; // true
const leftMost = bst.getLeftMost();
leftMost?.id === 1; // true
expect(leftMost?.id).toBe(1);
bst.remove(6);
bst.get(6); // null
bst.isAVLBalanced(); // true or false
const bfsIDs = bst.BFS();
bfsIDs[0] === 11; // true
expect(bfsIDs[0]).toBe(11);
const objBST = new BST();
objBST.add(11, {id: 11, keyA: 11});
objBST.add(3, {id: 3, keyA: 3});
objBST.addMany([{id: 15, keyA: 15}, {id: 1, keyA: 1}, {id: 8, keyA: 8},
{id: 13, keyA: 13}, {id: 16, keyA: 16}, {id: 2, keyA: 2},
{id: 6, keyA: 6}, {id: 9, keyA: 9}, {id: 12, keyA: 12},
{id: 14, keyA: 14}, {id: 4, keyA: 4}, {id: 7, keyA: 7},
{id: 10, keyA: 10}, {id: 5, keyA: 5}]);
objBST.remove(11);
const avlTree = new AVLTree();
avlTree.addMany([11, 3, 15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5])
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
avlTree.remove(10);
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
AVLTree snippet
TS
import {AVLTree} from 'data-structure-typed';
const avlTree = new AVLTree();
avlTree.addMany([11, 3, 15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5])
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
avlTree.remove(10);
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
JS
const {AVLTree} = require('data-structure-typed');
const avlTree = new AVLTree();
avlTree.addMany([11, 3, 15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5])
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
avlTree.remove(10);
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
Directed Graph simple snippet
TS or JS
import {DirectedGraph} from 'data-structure-typed';
const graph = new DirectedGraph();
graph.addVertex('A');
graph.addVertex('B');
graph.hasVertex('A'); // true
graph.hasVertex('B'); // true
graph.hasVertex('C'); // false
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.hasEdge('A', 'B'); // true
graph.hasEdge('B', 'A'); // false
graph.removeEdgeSrcToDest('A', 'B');
graph.hasEdge('A', 'B'); // false
graph.addVertex('C');
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.addEdge('B', 'C');
const topologicalOrderIds = graph.topologicalSort(); // ['A', 'B', 'C']
Undirected Graph snippet
TS or JS
import {UndirectedGraph} from 'data-structure-typed';
const graph = new UndirectedGraph();
graph.addVertex('A');
graph.addVertex('B');
graph.addVertex('C');
graph.addVertex('D');
graph.removeVertex('C');
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.addEdge('B', 'D');
const dijkstraResult = graph.dijkstra('A');
Array.from(dijkstraResult?.seen ?? []).map(vertex => vertex.id) // ['A', 'B', 'D']
Data Structures
| Data Structure | Unit Test | Performance Test | API Documentation | Implemented |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binary Tree |  |
 |
Binary Tree |  |
| Binary Search Tree (BST) |  |
 |
BST |  |
| AVL Tree |  |
 |
AVLTree |  |
| Tree Multiset |  |
 |
TreeMultiset |  |
| Segment Tree | SegmentTree |  |
||
| Binary Indexed Tree |  |
BinaryIndexedTree |  |
|
| Graph |  |
 |
AbstractGraph |  |
| Directed Graph |  |
 |
DirectedGraph |  |
| Undirected Graph |  |
 |
UndirectedGraph |  |
| Linked List |  |
 |
SinglyLinkedList |  |
| Singly Linked List |  |
 |
SinglyLinkedList |  |
| Doubly Linked List |  |
 |
DoublyLinkedList |  |
| Queue |  |
 |
Queue |  |
| Object Deque |  |
 |
ObjectDeque |  |
| Array Deque |  |
 |
ArrayDeque |  |
| Stack |  |
Stack |  |
|
| Coordinate Set | CoordinateSet |  |
||
| Coordinate Map | CoordinateMap |  |
||
| Heap |  |
 |
Heap |  |
| Priority Queue |  |
 |
PriorityQueue |  |
| Max Priority Queue |  |
 |
MaxPriorityQueue |  |
| Min Priority Queue |  |
 |
MinPriorityQueue |  |
| Trie |  |
Trie |  |



Why
Code design
By strictly adhering to object-oriented design (BinaryTree -> BST -> AVLTree -> TreeMultiset), you can seamlessly inherit the existing data structures to implement the customized ones you need. Object-oriented design stands as the optimal approach to data structure design.
Complexities
performance of Big O
| Big O Notation | Type | Computations for 10 elements | Computations for 100 elements | Computations for 1000 elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O(1) | Constant | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| O(log N) | Logarithmic | 3 | 6 | 9 |
| O(N) | Linear | 10 | 100 | 1000 |
| O(N log N) | n log(n) | 30 | 600 | 9000 |
| O(N^2) | Quadratic | 100 | 10000 | 1000000 |
| O(2^N) | Exponential | 1024 | 1.26e+29 | 1.07e+301 |
| O(N!) | Factorial | 3628800 | 9.3e+157 | 4.02e+2567 |
Data Structure Complexity
| Data Structure | Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Array | 1 | n | n | n | |
| Stack | n | n | 1 | 1 | |
| Queue | n | n | 1 | 1 | |
| Linked List | n | n | 1 | n | |
| Hash Table | - | n | n | n | In case of perfect hash function costs would be O(1) |
| Binary Search Tree | n | n | n | n | In case of balanced tree costs would be O(log(n)) |
| B-Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | |
| Red-Black Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | |
| AVL Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | |
| Bloom Filter | - | 1 | 1 | - | False positives are possible while searching |
Sorting Complexity
| Name | Best | Average | Worst | Memory | Stable | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bubble sort | n | n2 | n2 | 1 | Yes | |
| Insertion sort | n | n2 | n2 | 1 | Yes | |
| Selection sort | n2 | n2 | n2 | 1 | No | |
| Heap sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n log(n) | 1 | No | |
| Merge sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n log(n) | n | Yes | |
| Quick sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n2 | log(n) | No | Quicksort is usually done in-place with O(log(n)) stack space |
| Shell sort | n log(n) | depends on gap sequence | n (log(n))2 | 1 | No | |
| Counting sort | n + r | n + r | n + r | n + r | Yes | r - biggest number in array |
| Radix sort | n * k | n * k | n * k | n + k | Yes | k - length of longest key |


