| .github | ||
| scripts | ||
| src | ||
| test | ||
| .auto-changelog | ||
| .auto-changelog-template.hbs | ||
| .dependency-cruiser.js | ||
| .editorconfig | ||
| .eslintrc.js | ||
| .gitattributes | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .npmignore | ||
| .npmrc | ||
| .prettierignore | ||
| .prettierrc.js | ||
| .travis.yml | ||
| CHANGELOG.md | ||
| CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md | ||
| COMMANDS.md | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| jest.config.js | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| package-lock.json | ||
| package.json | ||
| README.md | ||
| SECURITY.md | ||
| tsconfig-base.json | ||
| tsconfig-cjs.json | ||
| tsconfig.json | ||
| tsup.config.js | ||
| webpack.config.js | ||
Data Structure Typed
Data Structures of Javascript & TypeScript.
Do you envy C++ with std, Python with collections, and Java with java.util ? Well, no need to envy anymore! JavaScript and TypeScript now have data-structure-typed.
Now you can use this library in Node.js and browser environments in CommonJS(require export.modules = ), ESModule(import export), Typescript(import export), UMD(var Queue = dataStructureTyped.Queue)
Built-in classic algorithms
DFS(Depth-First Search), DFSIterative, BFS(Breadth-First Search), morris, Bellman-Ford Algorithm, Dijkstra's Algorithm, Floyd-Warshall Algorithm, Tarjan's Algorithm.
Installation and Usage
npm
npm i data-structure-typed --save
yarn
yarn add data-structure-typed
import {
BinaryTree, Graph, Queue, Stack, PriorityQueue, BST, Trie, DoublyLinkedList,
AVLTree, MinHeap, SinglyLinkedList, DirectedGraph, TreeMultiset,
DirectedVertex, AVLTreeNode
} from 'data-structure-typed';
CDN
<script src='https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/data-structure-typed/dist/umd/data-structure-typed.min.js'></script>
const {Heap} = dataStructureTyped;
const {
BinaryTree, Graph, Queue, Stack, PriorityQueue, BST, Trie, DoublyLinkedList,
AVLTree, MinHeap, SinglyLinkedList, DirectedGraph, TreeMultiset,
DirectedVertex, AVLTreeNode
} = dataStructureTyped;
API docs & Examples
Code Snippet
Binary Search Tree (BST) snippet
TS
import {BST, BSTNode} from 'data-structure-typed';
const bst = new BST();
bst.add(11);
bst.add(3);
bst.addMany([15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5]);
bst.size === 16; // true
bst.has(6); // true
const node6 = bst.get(6); // BSTNode
bst.getHeight(6) === 2; // true
bst.getHeight() === 5; // true
bst.getDepth(6) === 3; // true
bst.getLeftMost()?.id === 1; // true
bst.remove(6);
bst.get(6); // null
bst.isAVLBalanced(); // true
bst.bfs()[0] === 11; // true
const objBST = new BST<BSTNode<{id: number, keyA: number}>>();
objBST.add(11, {id: 11, keyA: 11});
objBST.add(3, {id: 3, keyA: 3});
objBST.addMany([{id: 15, keyA: 15}, {id: 1, keyA: 1}, {id: 8, keyA: 8},
{id: 13, keyA: 13}, {id: 16, keyA: 16}, {id: 2, keyA: 2},
{id: 6, keyA: 6}, {id: 9, keyA: 9}, {id: 12, keyA: 12},
{id: 14, keyA: 14}, {id: 4, keyA: 4}, {id: 7, keyA: 7},
{id: 10, keyA: 10}, {id: 5, keyA: 5}]);
objBST.remove(11);
JS
const {BST, BSTNode} = require('data-structure-typed');
const bst = new BST();
bst.add(11);
bst.add(3);
bst.addMany([15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5]);
bst.size === 16; // true
bst.has(6); // true
const node6 = bst.get(6);
bst.getHeight(6) === 2; // true
bst.getHeight() === 5; // true
bst.getDepth(6) === 3; // true
const leftMost = bst.getLeftMost();
leftMost?.id === 1; // true
expect(leftMost?.id).toBe(1);
bst.remove(6);
bst.get(6); // null
bst.isAVLBalanced(); // true or false
const bfsIDs = bst.bfs();
bfsIDs[0] === 11; // true
expect(bfsIDs[0]).toBe(11);
const objBST = new BST();
objBST.add(11, {id: 11, keyA: 11});
objBST.add(3, {id: 3, keyA: 3});
objBST.addMany([{id: 15, keyA: 15}, {id: 1, keyA: 1}, {id: 8, keyA: 8},
{id: 13, keyA: 13}, {id: 16, keyA: 16}, {id: 2, keyA: 2},
{id: 6, keyA: 6}, {id: 9, keyA: 9}, {id: 12, keyA: 12},
{id: 14, keyA: 14}, {id: 4, keyA: 4}, {id: 7, keyA: 7},
{id: 10, keyA: 10}, {id: 5, keyA: 5}]);
objBST.remove(11);
const avlTree = new AVLTree();
avlTree.addMany([11, 3, 15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5])
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
avlTree.remove(10);
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
AVLTree snippet
TS
import {AVLTree} from 'data-structure-typed';
const avlTree = new AVLTree();
avlTree.addMany([11, 3, 15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5])
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
avlTree.remove(10);
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
JS
const {AVLTree} = require('data-structure-typed');
const avlTree = new AVLTree();
avlTree.addMany([11, 3, 15, 1, 8, 13, 16, 2, 6, 9, 12, 14, 4, 7, 10, 5])
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
avlTree.remove(10);
avlTree.isAVLBalanced(); // true
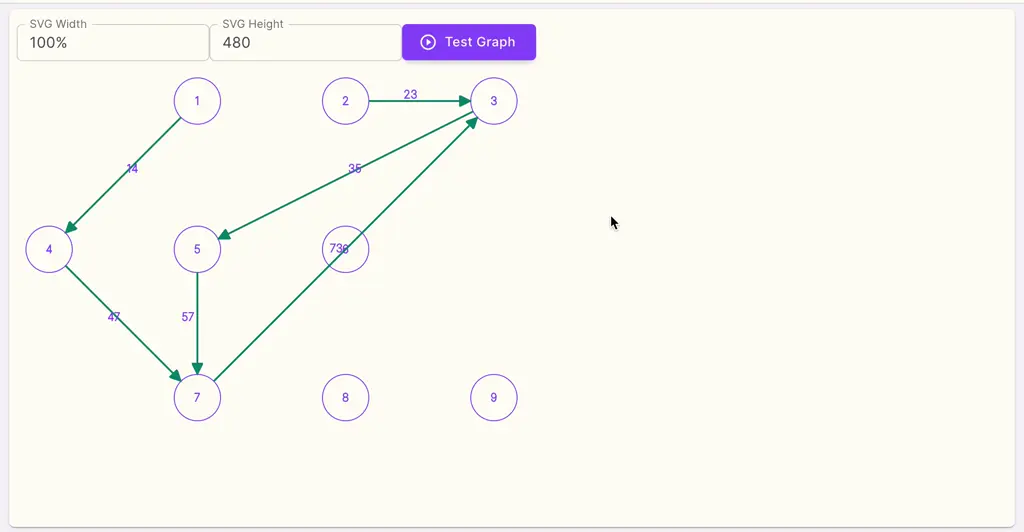
Directed Graph simple snippet
TS or JS
import {DirectedGraph} from 'data-structure-typed';
const graph = new DirectedGraph();
graph.addVertex('A');
graph.addVertex('B');
graph.hasVertex('A'); // true
graph.hasVertex('B'); // true
graph.hasVertex('C'); // false
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.hasEdge('A', 'B'); // true
graph.hasEdge('B', 'A'); // false
graph.removeEdgeSrcToDest('A', 'B');
graph.hasEdge('A', 'B'); // false
graph.addVertex('C');
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.addEdge('B', 'C');
const topologicalOrderIds = graph.topologicalSort(); // ['A', 'B', 'C']
Undirected Graph snippet
TS or JS
import {UndirectedGraph} from 'data-structure-typed';
const graph = new UndirectedGraph();
graph.addVertex('A');
graph.addVertex('B');
graph.addVertex('C');
graph.addVertex('D');
graph.removeVertex('C');
graph.addEdge('A', 'B');
graph.addEdge('B', 'D');
const dijkstraResult = graph.dijkstra('A');
Array.from(dijkstraResult?.seen ?? []).map(vertex => vertex.id) // ['A', 'B', 'D']
Data Structures
| Data Structure | Unit Test | Performance Test | API Documentation | Implemented |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binary Tree |  |
 |
Binary Tree |  |
| Binary Search Tree (BST) |  |
 |
BST |  |
| AVL Tree |  |
 |
AVLTree |  |
| Tree Multiset |  |
 |
TreeMultiset |  |
| Segment Tree | SegmentTree |  |
||
| Binary Indexed Tree |  |
BinaryIndexedTree |  |
|
| Graph |  |
 |
AbstractGraph |  |
| Directed Graph |  |
 |
DirectedGraph |  |
| Undirected Graph |  |
 |
UndirectedGraph |  |
| Linked List |  |
 |
SinglyLinkedList |  |
| Singly Linked List |  |
 |
SinglyLinkedList |  |
| Doubly Linked List |  |
 |
DoublyLinkedList |  |
| Queue |  |
 |
Queue |  |
| Object Deque |  |
 |
ObjectDeque |  |
| Array Deque |  |
 |
ArrayDeque |  |
| Stack |  |
Stack |  |
|
| Coordinate Set | CoordinateSet |  |
||
| Coordinate Map | CoordinateMap |  |
||
| Heap |  |
 |
Heap |  |
| Priority Queue |  |
 |
PriorityQueue |  |
| Max Priority Queue |  |
 |
MaxPriorityQueue |  |
| Min Priority Queue |  |
 |
MinPriorityQueue |  |
| Trie |  |
Trie |  |
Standard library data structure comparison
| Data Structure | Data Structure Typed | C++ std | java.util | Python collections |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Array | Array<E> | vector<T> | ArrayList<E> | list |
| Linked List | DoublyLinkedList<E> | list<T> | LinkedList<E> | deque |
| Singly Linked List | SinglyLinkedList<E> | - | - | - |
| Set | Set<E> | set<T> | HashSet<E> | set |
| Map | Map<K, V> | map<K, V> | HashMap<K, V> | dict |
| Ordered Dictionary | Map<K, V> | - | - | OrderedDict |
| Queue | Queue<E> | queue<T> | Queue<E> | - |
| Priority Queue | PriorityQueue<E> | priority_queue<T> | PriorityQueue<E> | - |
| Heap | Heap<V> | priority_queue<T> | PriorityQueue<E> | heapq |
| Stack | Stack<E> | stack<T> | Stack<E> | - |
| Deque | Deque<E> | deque<T> | - | - |
| Trie | Trie | - | - | - |
| Unordered Map | HashMap<K, V> | unordered_map<K, V> | HashMap<K, V> | defaultdict |
| Multiset | - | multiset<T> | - | - |
| Multimap | - | multimap<K, V> | - | - |
| Binary Tree | BinaryTree<K, V> | - | - | - |
| Binary Search Tree | BST<K, V> | - | - | - |
| Directed Graph | DirectedGraph<V, E> | - | - | - |
| Undirected Graph | UndirectedGraph<V, E> | - | - | - |
| Unordered Multiset | - | unordered_multiset | - | Counter |
| Linked Hash Set | - | - | LinkedHashSet<E> | - |
| Linked Hash Map | - | - | LinkedHashMap<K, V> | - |
| Sorted Set | AVLTree<E> | - | TreeSet<E> | - |
| Sorted Map | AVLTree<K, V> | - | TreeMap<K, V> | - |
| Tree Set | AVLTree<E> | set | TreeSet<E> | - |
| Unordered Multimap | - | unordered_multimap<K, V> | - | - |
| Bitset | - | bitset<N> | - | - |
| Unordered Set | - | unordered_set<T> | HashSet<E> | - |
Code design
Adhere to ES6 standard naming conventions for APIs.
Standardize API conventions by using 'add' and 'delete' for element manipulation methods in all data structures.
Opt for concise and clear method names, avoiding excessive length while ensuring explicit intent.
Object-oriented programming(OOP)
By strictly adhering to object-oriented design (BinaryTree -> BST -> AVLTree -> TreeMultiset), you can seamlessly inherit the existing data structures to implement the customized ones you need. Object-oriented design stands as the optimal approach to data structure design.
Complexities
performance of Big O
| Big O Notation | Type | Computations for 10 elements | Computations for 100 elements | Computations for 1000 elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O(1) | Constant | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| O(log N) | Logarithmic | 3 | 6 | 9 |
| O(N) | Linear | 10 | 100 | 1000 |
| O(N log N) | n log(n) | 30 | 600 | 9000 |
| O(N^2) | Quadratic | 100 | 10000 | 1000000 |
| O(2^N) | Exponential | 1024 | 1.26e+29 | 1.07e+301 |
| O(N!) | Factorial | 3628800 | 9.3e+157 | 4.02e+2567 |
Data Structure Complexity
| Data Structure | Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Array | 1 | n | n | n | |
| Stack | n | n | 1 | 1 | |
| Queue | n | n | 1 | 1 | |
| Linked List | n | n | 1 | n | |
| Hash Table | - | n | n | n | In case of perfect hash function costs would be O(1) |
| Binary Search Tree | n | n | n | n | In case of balanced tree costs would be O(log(n)) |
| B-Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | |
| Red-Black Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | |
| AVL Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | |
| Bloom Filter | - | 1 | 1 | - | False positives are possible while searching |
Sorting Complexity
| Name | Best | Average | Worst | Memory | Stable | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bubble sort | n | n2 | n2 | 1 | Yes | |
| Insertion sort | n | n2 | n2 | 1 | Yes | |
| Selection sort | n2 | n2 | n2 | 1 | No | |
| Heap sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n log(n) | 1 | No | |
| Merge sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n log(n) | n | Yes | |
| Quick sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n2 | log(n) | No | Quicksort is usually done in-place with O(log(n)) stack space |
| Shell sort | n log(n) | depends on gap sequence | n (log(n))2 | 1 | No | |
| Counting sort | n + r | n + r | n + r | n + r | Yes | r - biggest number in array |
| Radix sort | n * k | n * k | n * k | n + k | Yes | k - length of longest key |